My colleague David asked about a very interesting feature.
"What if we can provision Azure Static Web App and deploy the app at the same time? If we can, we just simply hand over our PoC repository to developers so that they just run it directly from there."
Although two challenges exist to achieve this idea, if we can combine both challenges, devs can autopilot everything from the resource creating to the app deployment, which will result in improving the development experiences. Throughout this post, I'm going to discuss how to offer the autopilot feature for your application repository.
You can download the sample code from this repository.
Architecture
- Front-end Application: Blazor Web Assembly
- Back-end Application: Azure Functions
- Database: Cosmos DB
Both front-end and back-end apps can be combined with Azure Static Web Apps (ASWA), and both ASWA and Cosmos DB are provisioned through GitHub Actions. So the overall architecture might look like this:
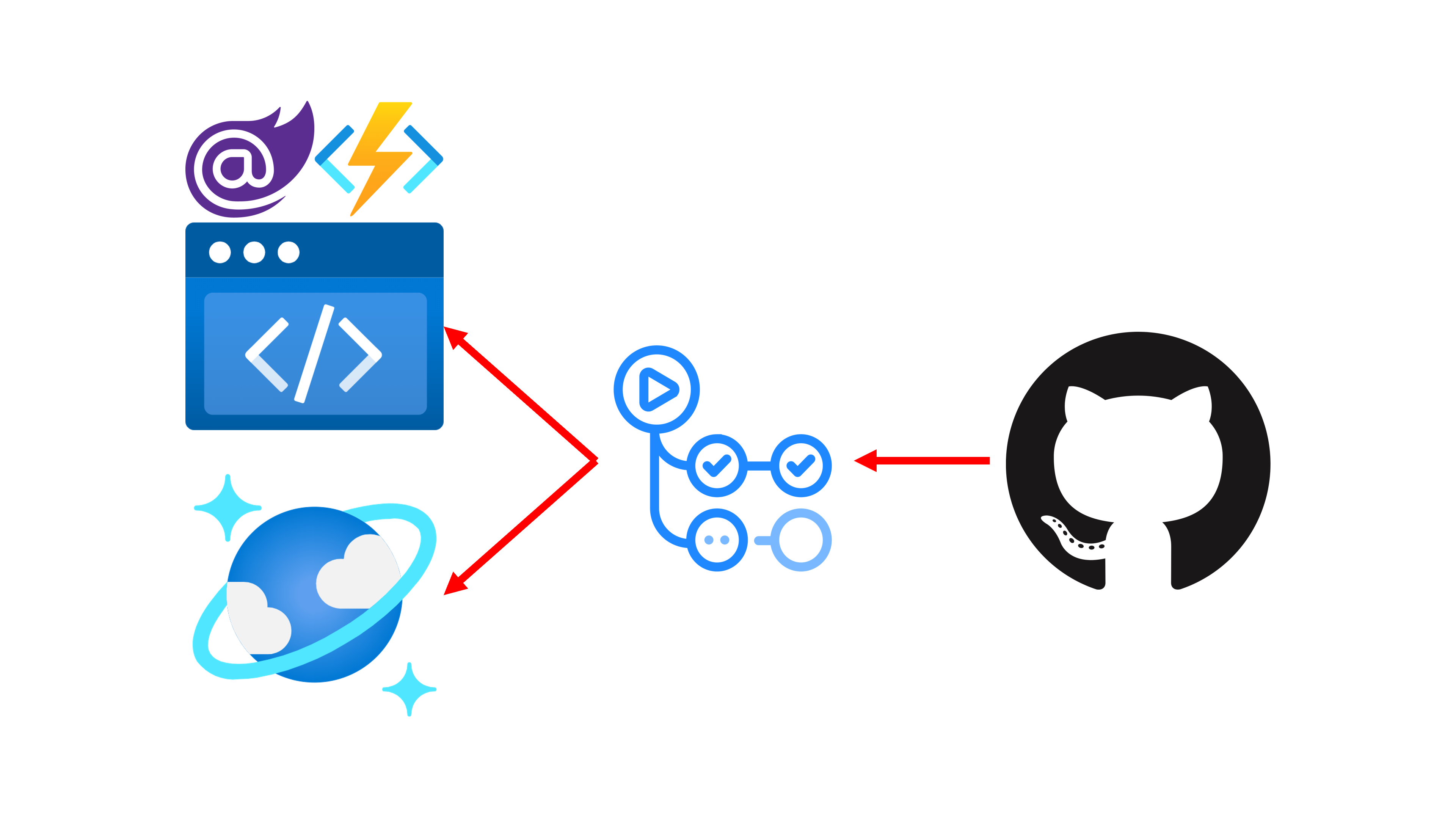
Azure Resource Provisioning
Let's build Azure resources based on the architecture diagram above. Azure Bicep would be the choice for resource provisioning.
Cosmos DB
First of all, declare Cosmos DB instance. We're going to use the Serverless tier and the SQL API, give the database name of AdventureWorks and the container name of products. Here's the sample Bicep file. For brevity, irrelevant details are omitted.
// cosmosDb.bicep: Cosmos DB
param resourceName string
param resourceLocation string
param databaseName string
param containerName string
resource cosdba 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts@2021-10-15' = {
name: 'cosdba-${resourceName}'
location: resourceLocation
kind: 'GlobalDocumentDB'
properties: {
...
capabilities: [
{
name: 'EnableServerless'
}
]
...
}
}
resource cosdbasql 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases@2021-10-15' = {
name: '${cosdba.name}/${databaseName}'
properties: {
resource: {
id: databaseName
}
}
}
resource cosdbasqlcontainer 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases/containers@2021-10-15' = {
name: '${cosdbasql.name}/${containerName}'
properties: {
resource: {
id: containerName
partitionKey: {
paths: [
'/category'
]
}
}
}
}
// Outputs
output connectionString string = 'AccountEndpoint=https://${cosdba.name}.documents.azure.com:443/;AccountKey=${cosdba.listKeys().primaryMasterKey};'When you see the output value at the bottom line, it uses the listKeys() function that returns the connection string of the Cosmos DB instance. This value will be used for ASWA integration.
Azure Static Web Apps
Let's declare ASWA instance. This time, we use the basic free tier and add the Cosmos DB connection string for the back-end API to use. Without unnecessary details, the Bicep file might look like this:
// staticWebApp.bicep: Azure Static Web Apps
param resourceName string
param resourceLocation string
@secure()
param cosmosDbConnectionString string
resource sttapp 'Microsoft.Web/staticSites@2021-03-01' = {
name: 'sttapp-${resourceName}'
location: resourceLocation
sku: {
name: 'Free'
}
...
}
resource sttappconfig 'Microsoft.Web/staticSites/config@2021-03-01' = {
name: '${sttapp.name}/appsettings'
properties: {
ConnectionStrings_CosmosDB: cosmosDbConnectionString
}
}
// Outputs
output deploymentKey string = sttapp.listSecrets().properties.apiKeyThe output value at the bottom line uses the listSecreets() function to return the deployment key for the CI/CD pipeline to use. This value will be used while deploying the app within the GitHub Actions workflow.
main.bicep – Orchestration
We've got both Cosmos DB and ASWA instances declared by Bicep. Now, we need the orchestration file to create both resources. Here's the script. It uses the module keyword to call the pre-defined resources.
// main.bicep: Orchestration
param resourceName string
param cosmosDbLocation string
param cosmosDbDatabaseName string
param cosmosDbContainerName string
param staticAppLocation string
// Cosmos DB
module cosdba './cosmosDb.bicep' = {
name: 'CosmosDB'
params: {
resourceName: resourceName
location: cosmosDbLocation
databaseName: cosmosDbDatabaseName
containerName: cosmosDbContainerName
}
}
// Static Web App
module sttapp './staticWebApp.bicep' = {
name: 'StaticWebApp'
params: {
resourceName: resourceName
location: staticAppLocation
cosmosDbConnectionString: cosdba.outputs.connectionString
}
}
// Outputs
output connectionString string = cosdba.outputs.connectionString
output deploymentKey string = sttapp.outputs.deploymentKeyThe output values return the Cosmos DB connection string and ASWA deployment key.
azuredeploy.bicep – Subscription Level Scope
Although we can use the main.bicep for resource creation, we also need to provision the resource group for the "autopilot" feature. Therefore, let's create the azuredeploy.bicep that creates the resource group and provisions resources into the resource group. In this file, the first line should declare the targetScope value as subscription.
Because this Bicep file offers the autopilot feature, it minimises user interventions by providing possible options. The following Bicep file shows how to give options to developers to choose, except resourceName.
// azuredeploy.bicep
targetScope = 'subscription'
param name string
@allowed([
...
'Central US'
'East Asia'
'East US 2'
'Korea Central'
'West Europe'
'West US 2'
...
])
param cosmosDbLocation string = 'Korea Central'
param cosmosDbDatabaseName string = 'AdventureWorks'
param cosmosDbContainerName string = 'products'
@allowed([
'Central US'
'East Asia'
'East US 2'
'West Europe'
'West US 2'
])
param staticAppLocation string = 'East Asia'
// Resource Group
resource rg 'Microsoft.Resources/resourceGroups@2021-04-01' = {
name: 'rg-${name}'
location: cosmosDbLocation
}
// Resource Orchestration
module resources './main.bicep' = {
name: 'Resources'
scope: rg
params: {
resourceName: name
cosmosDbLocation: rg.location
cosmosDbDatabaseName: cosmosDbDatabaseName
cosmosDbContainerName: cosmosDbContainerName
staticAppLocation: staticAppLocation
}
}
// Outputs
output connectionString string = resources.outputs.connectionString
output deploymentKey string = resources.outputs.deploymentKeyThe output values represent the Cosmos DB connection string and the ASWA deployment key.
We're almost there! Run the following command to convert azuredeploy.bicep to azuredeploy.json ARM template for Azure Portal to understand.
az bicep build -f azuredeploy.bicepNOTE: Each Bicep file above represents individual resource, orchestration and subscription level scoping, respectively, based on my preference - single responsibility principle. But you can build up one massive
azuredeploy.bicepif you like.
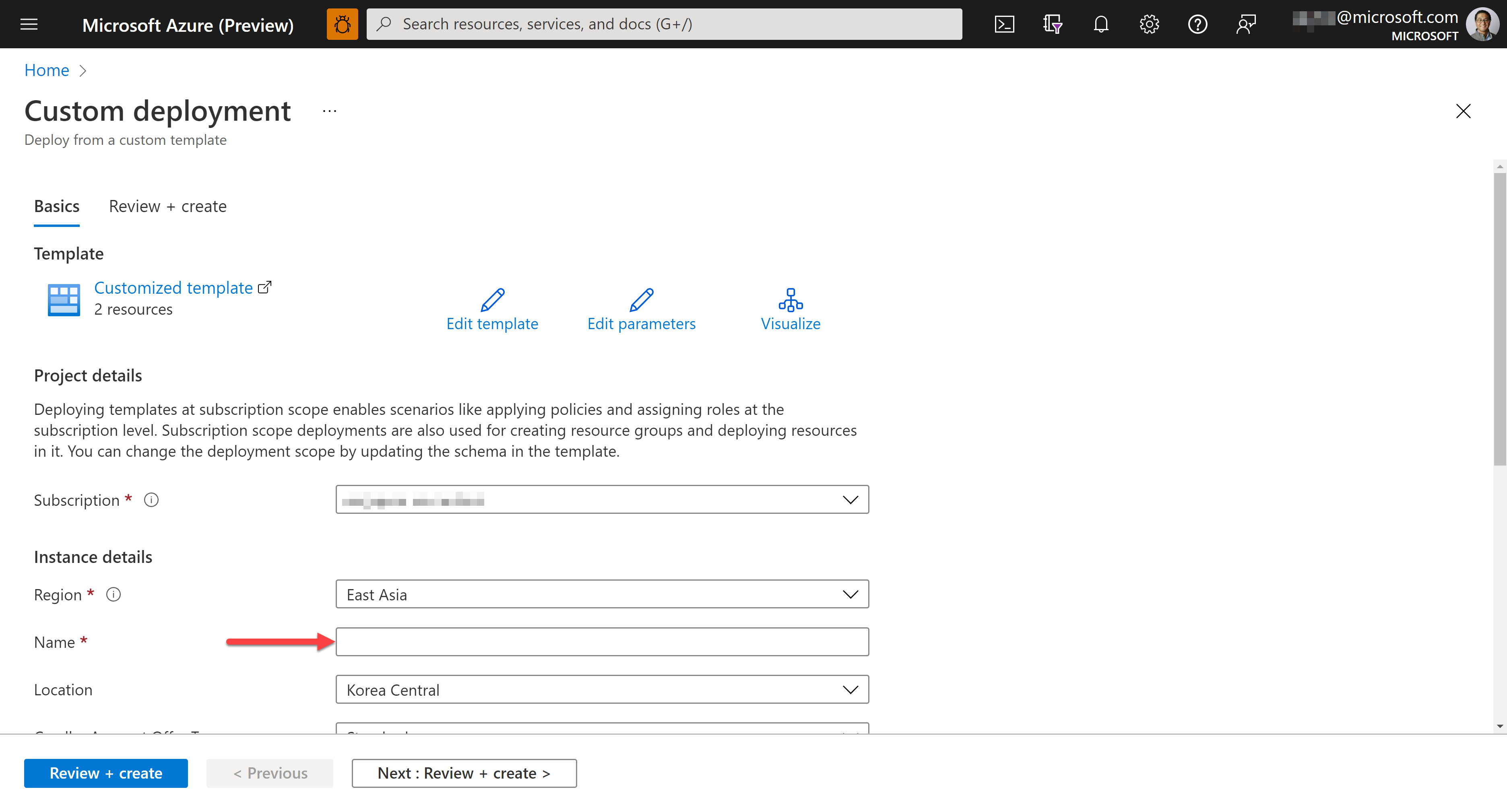
Once the ARM template, azuredeploy.json, is generated, connect its GitHub URL to the "Deploy to Azure" button.
You will see the Azure Portal screen that provision resources when you click the button above. All the rest fields have already been filled with default values, except the Name field.
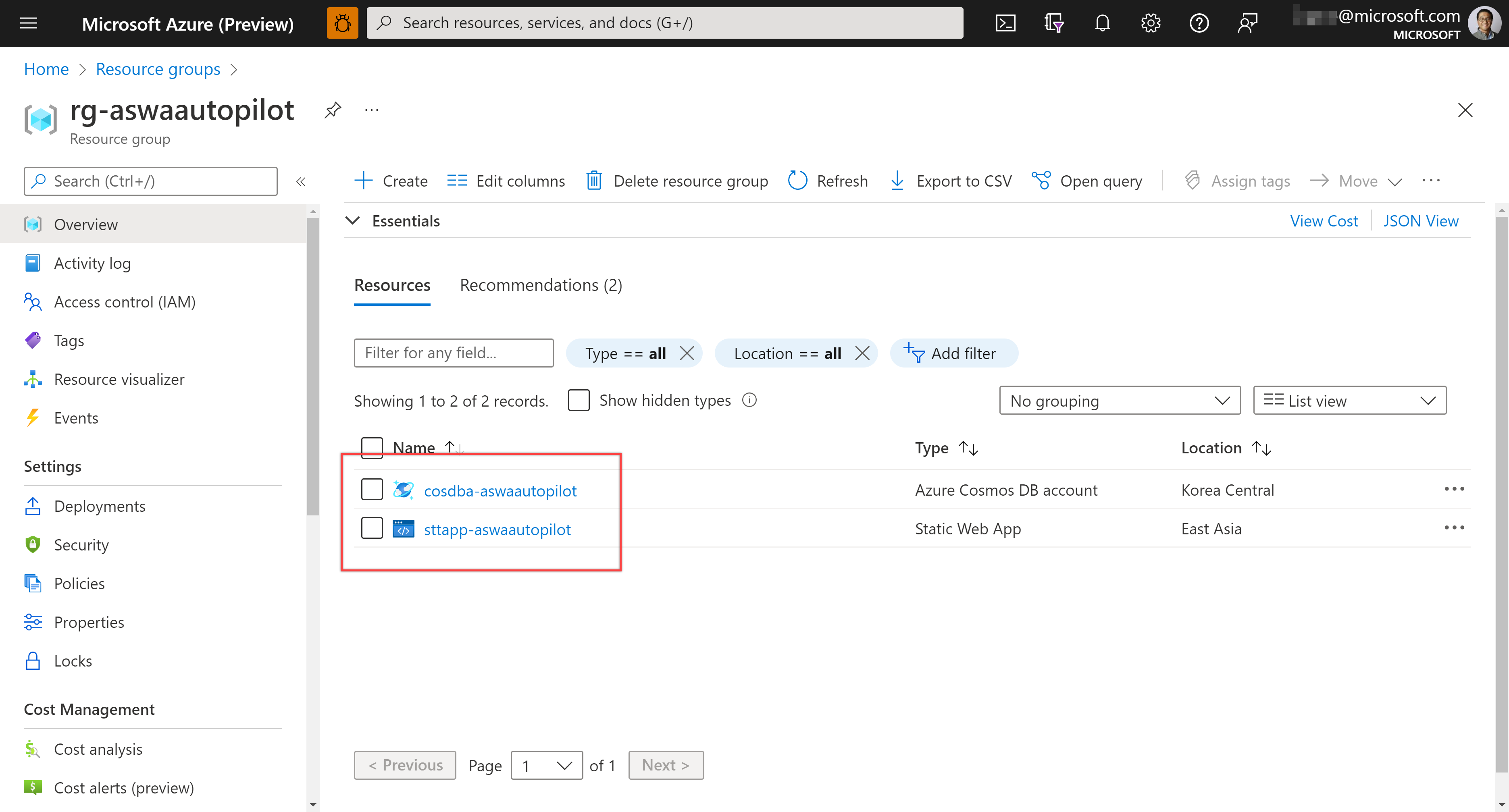
Once provisioning completes, you will be able to see the resources on Azure Portal:
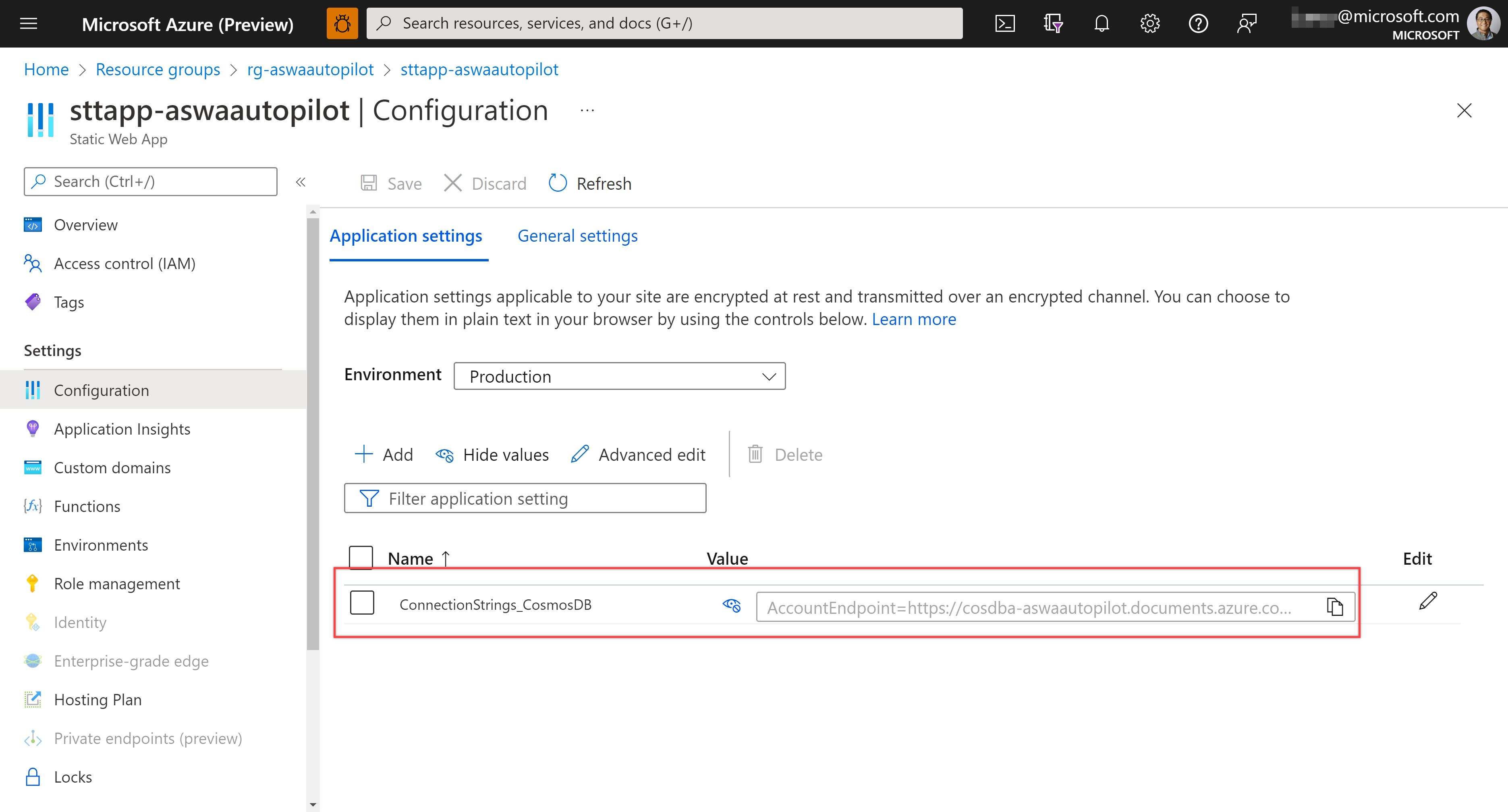
ASWA contains the Cosmos DB connection string as well.
So far, we've completed the resource provisioning. However, we still need the app deployment. Let's move on.
Azure App Deployment
To deploy ASWA to Azure, CI/CD pipeline is the only way at the time of this writing. Therefore, it's critical to rely on GitHub Actions workflow. What if we want to use the CI/CD pipeline from the other vendors? We should decouple this GitHub Actions dependency first.
Fortunately, our provisioned ASWA instance hasn't got connected to any CI/CD pipeline yet, but it has the deployment key for other CI/CD pipelines to use. With this key, we can connect our own GitHub Actions workflow. So let's use this deployment key to connect the GitHub Actions workflow controlled by us.
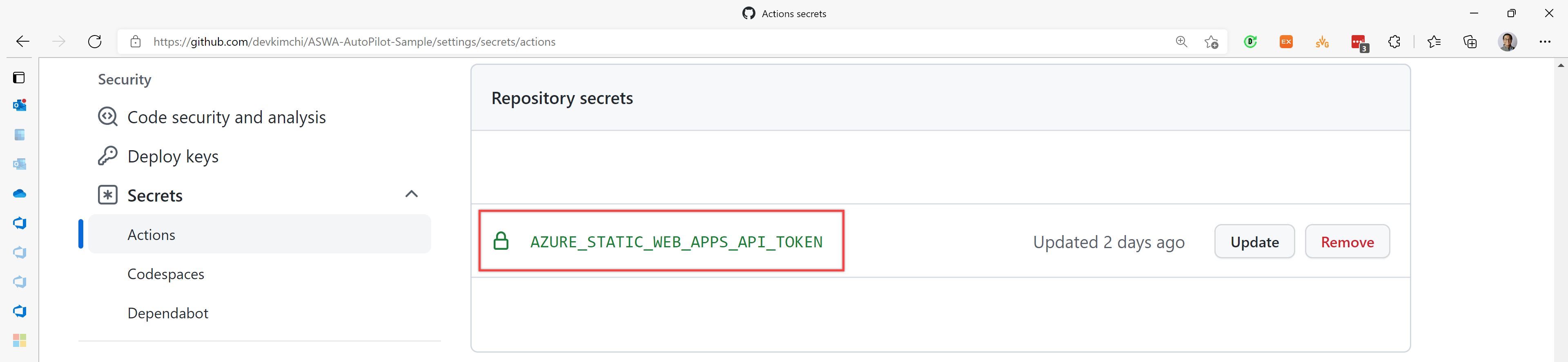
Deployment Key as GitHub Secret
Let's store the deployment key to GitHub secret, AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN.
GitHub Actions Workflow – workflow_call
There are roughly two events for the app deployment.
- After code changes:
pushorpull_request - After resource provisioning through autopilot:
workflow_dispatch
As we need to deploy the app in both cases, workflow_call is the best bet to be called from both events. The following workflow shows how to write the workflow. The caller workflow passes parameters and secrets and executes the Azure/static-web-apps-deploy action. Because all the parameter values have their defaults, the caller workflow only needs to pass the secrets.
# app-deploy.yaml
name: 'App Deploy'
on:
workflow_call:
inputs:
job_name:
type: string
required: false
default: 'Deploy Static Web App'
app_location:
type: string
required: false
default: app
api_location:
type: string
required: false
default: api
output_location:
type: string
required: false
default: wwwroot
secrets:
gh_token:
required: true
aswa_token:
required: true
jobs:
deploy:
name: ${{ inputs.job_name }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout the repo
uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
submodules: true
- name: Deploy Static Web App
uses: Azure/static-web-apps-deploy@v1
with:
azure_static_web_apps_api_token: ${{ secrets.aswa_token }}
repo_token: ${{ secrets.gh_token }}
action: upload
app_location: ${{ inputs.app_location }}
api_location: ${{ inputs.api_location }}
output_location: ${{ inputs.output_location }}GitHub Actions Workflow – workflow_dispatch
Through this workflow_dispatch workflow, we can call the workflow_call workflow, app-deploy.yaml, outside GitHub or other workflows. Here's the sample workflow. All parameters are the same as the ones in app-deploy.yaml, except their namings.
# main-dispatch.yaml
name: 'App Deploy Dispatch'
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
jobName:
type: string
description: Job name
required: false
default: 'Deploy Static Web App'
appLocation:
type: string
description: Web app location
required: false
default: app
apiLocation:
type: string
description: API app location
required: false
default: api
outputLocation:
type: string
description: Web app artifact location
required: false
default: wwwroot
jobs:
call_app_deploy:
uses: devkimchi/ASWA-AutoPilot-Sample/.github/workflows/app-deploy.yaml@main
with:
job_name: ${{ github.event.inputs.jobName }}
app_location: ${{ github.event.inputs.appLocation }}
api_location: ${{ github.event.inputs.apiLocation }}
output_location: ${{ github.event.inputs.outputLocation }}
secrets:
gh_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
aswa_token: '${{ secrets.AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN }}'As you can see, the call_app_deploy job calls the workflow defined in app-deploy.yaml with parameters and secrets.
Once completed, run the following GitHub CLI command on your terminal, which calls the workflow_dispatch event, main-dispatch.yaml.
gh workflow run "App Deploy Dispatch" \
--repo devkimchi/ASWA-AutoPilot-SampleNOTE: To run the GitHub CLI command above, you should be logged in beforehand. If you're unsure, run the
gh auth statuscommand to make sure whether you're already logged in or not. Then, run thegh auth logincommand to log in if you're logged out.
You're now able to deploy the app after the resource provisioning.
GitHub Actions Workflow – push/pull_request
You've deployed the app for the first time through the autopilot feature. Now, you've got the code changes. Then, you also need another workflow reacting both push and pull_request events. As you've already got the workflow_call workflow, app-deploy.yaml, you only need a wrapper workflow for it. Here's the one:
# main-app.yaml
name: 'App Deploy'
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
- closed
branches:
- main
jobs:
call_app_deploy:
if: github.event_name == 'push' || (github.event_name == 'pull_request' && github.event.action != 'closed')
uses: devkimchi/ASWA-AutoPilot-Sample/.github/workflows/app-deploy.yaml@main
with:
job_name: 'Deploy Static Web App'
app_location: 'app'
api_location: 'api'
output_location: 'wwwroot'
secrets:
gh_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
aswa_token: '${{ secrets.AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN }}'This workflow is triggered by either push or pull_request. With this workflow, when you change your code, it will be deployed through this main-app.yaml workflow.
Putting Altogether
By the way, I'm still not happy about it because it's the TWO-STEP process. Can we merge two operations in one? The most realistic scenario at this time of writing is that we make use of the workflow_dispatch event that provisions the resources and deploys the app. Let's move on.
GitHub Actions Workflow – Resource Provisioning
We've already got all the necessary Bicep files. Therefore, write another workflow_call workflow to run the Bicep file. Here's the sample workflow. Except for the resource_name parameter, all parameters have default values.
# resource-provision.yaml
name: 'Resource Provision'
on:
workflow_call:
inputs:
job_name:
type: string
required: false
default: 'Provision Resources'
resource_name:
type: string
required: true
cosdba_location:
type: string
required: false
default: 'Korea Central'
sttapp_location:
type: string
required: false
default: 'East Asia'
secrets:
pa_token:
required: true
az_credentials:
required: true
jobs:
deploy:
name: ${{ inputs.job_name }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout the repo
uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
submodules: true
- name: Login to Azure
uses: Azure/login@v1
with:
creds: ${{ secrets.az_credentials }}
- name: Provision resources
id: provisioned
shell: pwsh
run: |
cd ./infra
$result = ./Provision-Resources.ps1 `
-ResourceName "${{ inputs.resource_name}}" `
-Location "${{ inputs.cosdba_location }}" `
-CosmosDbPrimaryRegion "${{ inputs.cosdba_location }}" `
-StaticWebAppLocation "${{ inputs.sttapp_location }}" `
-TargetScope Subscription
$provisioned = $result | ConvertFrom-Json
$deploymentKey = $provisioned.properties.outputs.sttappDeploymentKey.value
echo "::add-mask::$deploymentKey"
echo "::set-output name=sttapp_deploymentkey::$deploymentKey"
- name: Update GitHub repository secrets
uses: hmanzur/actions-set-secret@v2.0.0
with:
token: ${{ secrets.pa_token }}
repository: ${{ github.repository }}
name: AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN
value: ${{ steps.provisioned.outputs.sttapp_deploymentkey }}To provision resources to Azure, Azure CLI is required. The PowerShell script, Provision-Resources.ps1, has all the necessary details. This PowerShell script returns the provisioning details, including the ASWA deployment key. The deployment key is stored in GitHub secret at the final action.
GitHub Actions Workflow – Autopilot
Here's the last GitHub Actions workflow using the workflow_dispatch event. The input parameters provide as many options as possible to minimise user inputs, except for the resourceName parameter.
# main-autopilot.yaml
name: 'Autopilot'
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
resourceName:
type: string
description: 'Resource name'
required: true
location:
type: choice
description: 'Cosmos DB location. Default is "Korea Central"'
required: false
options:
...
- 'Central US'
- 'East Asia'
- 'East US 2'
- 'Korea Central'
- 'West Europe'
- 'West US 2'
...
default: 'Korea Central'
staticWebAppLocation:
type: choice
description: 'Static Web App location. Default is "East Asia".'
required: false
options:
- 'Central US'
- 'East Asia'
- 'East US 2'
- 'West Europe'
- 'West US 2'
default: 'East Asia'
jobs:
call_resource_provisioning:
uses: devkimchi/ASWA-AutoPilot-Sample/.github/workflows/resource-provision.yaml@main
with:
job_name: 'Provision Resources'
resource_name: ${{ github.event.inputs.resourceName }}
cosdba_location: ${{ github.event.inputs.location }}
sttapp_location: ${{ github.event.inputs.staticWebAppLocation }}
secrets:
pa_token: ${{ secrets.PA_TOKEN }}
az_credentials: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CREDENTIALS }}
call_workflow_dispatch:
needs: call_resource_provisioning
name: 'Deploy Static Web App'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Invoke workflow with inputs
uses: benc-uk/workflow-dispatch@v1
with:
workflow: 'App Deploy Dispatch'
token: ${{ secrets.PA_TOKEN }}
inputs: '{ "jobName": "Deploy Static Web App", "appLocation": "app", "apiLocation": "api", "outputLocation": "wwwroot" }'When you see the workflow above, the first job calls another workflow_call event, resource-provision.yaml, while the second job calls the workflow_dispatch event. So why does it call the workflow_dispatch event, main-dispatch.yaml instead of calling workflow_call event, app-deploy.yaml?
Unless you're using the deployment key stored in the first workflow_call job, resource-provision.yaml, the second job can use another workflow_call, app-deploy.yaml. However, any GitHub repository secret updates can't be recognised within the same pipeline context. Therefore, we need to create a new pipeline context by calling the workflow_dispatch event main-dispatch.yaml to get the newly stored ASWA deployment key.
We got the whole autopilot landscape. But we need two more steps – adding two secrets, AZURE_CREDENTIALS and PA_TOKEN.
It's safe to remove the existing secret,
AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN. The secret value will be automatically updated during the autopilot execution if you don't.
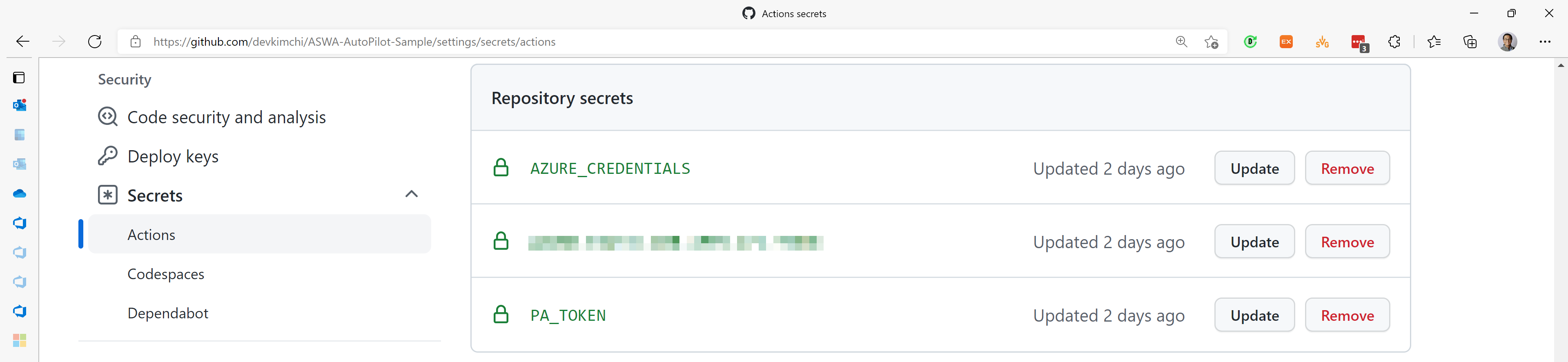
AZURE_CREDENTIALS
The workflow uses Azure CLI, which requires the login details. Run the following command to create the Azure login credentials and store it to AZURE_CREDENTIALS.
az ad sp create-for-rbac \
--name "myApp" \
--role contributor \
--sdk-authIf you want to know more details, refer to this document.
PA_TOKEN
The GitHub personal access token (PAT) is required to store the ASWA deployment key within the workflow_dispatch workflow and call the other workflow_dispatch event. Use this document to generate a PAT and store it to PA_TOKEN.
Autopilot Execution
Once all of the above is done, let's run the autopilot feature.
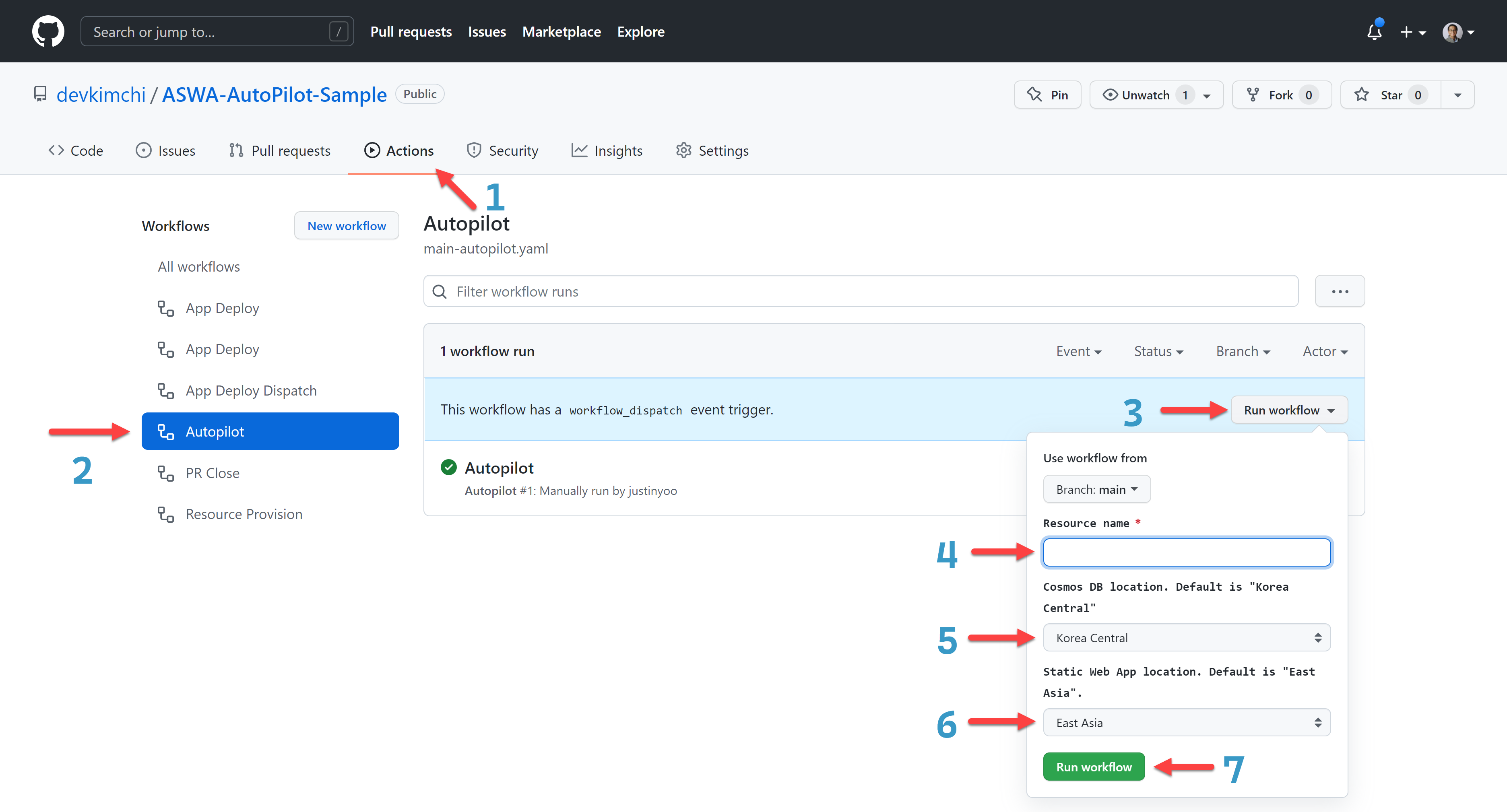
- Go to the "Actions" tab.
- Click the "Autopilot" tab.
- Click the "Run workflow" button.
- Enter the resource name.
- Choose the Cosmos DB location.
- Choose the Azure Static Web App location.
- Click the "Run workflow" button.
Once the autopilot is done, both resource provisioning and app deployment are completed at once. As you can see in the picture below, it's expected to see the "No product found" message because of no record stored in the Cosmos DB instance.
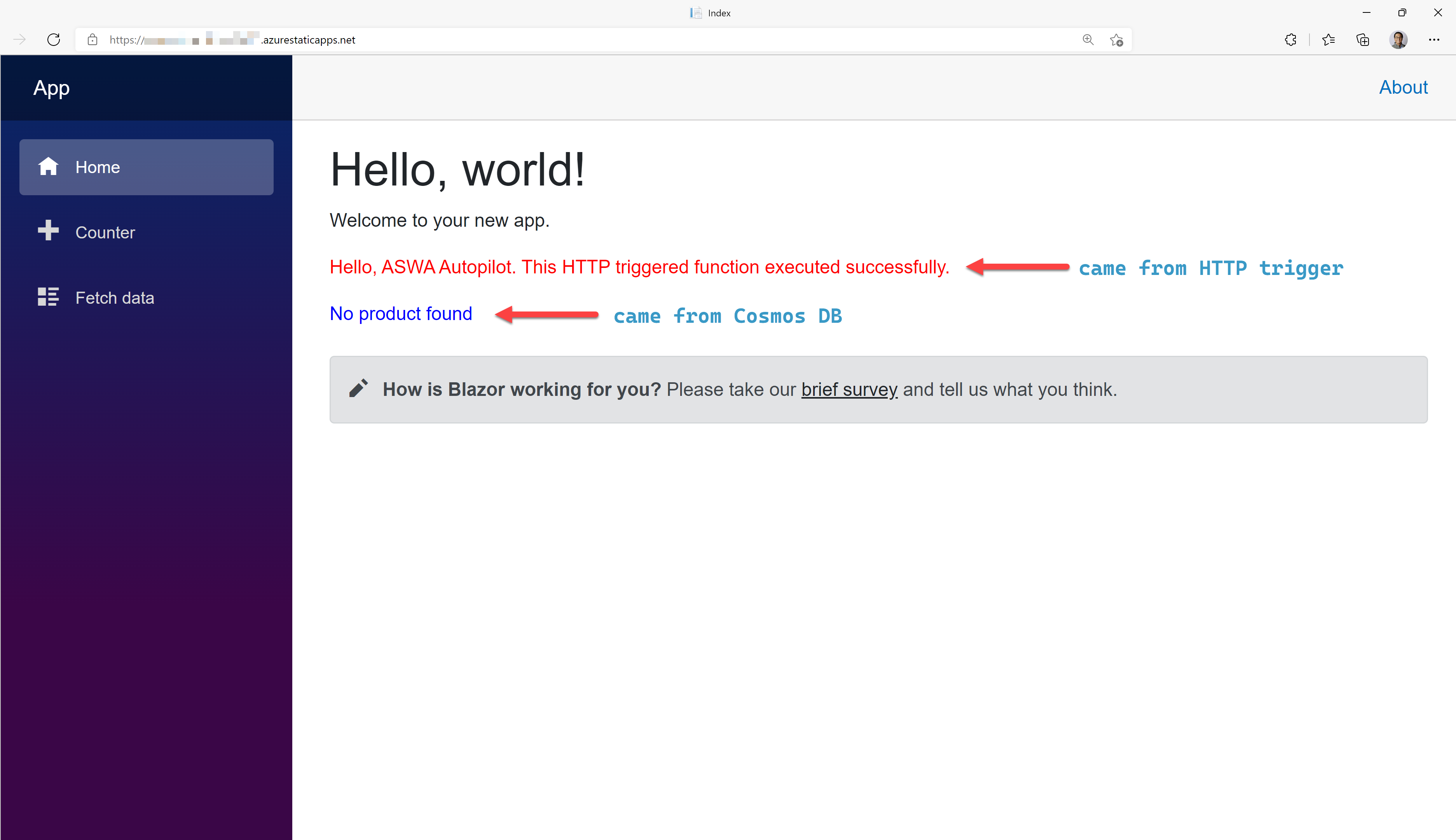
The autopilot feature is working as expected.
Known Issues for Improvements
Although we've implemented the autopilot feature through GitHub Actions workflow and Azure Bicep, there are a couple of things to sort out for better deployment experiences.
-
Manually storing Azure CLI and GitHub PAT to GitHub secrets
Azure CLI doesn't currently have the ASWA deployment feature yet. It has a spec, but no implementation is yet found, which I believe the implementation will soon be available. Once it's available, we wouldn't need the GitHub PAT any longer.
-
Using the "Deploy to Azure" button
Azure Bicep currently supports the Deployment Scripts feature. Through this feature, we can run Azure CLI directly from the Bicep file without having to know the Azure login details. Once Azure CLI is available to deploy ASWA, this would significantly improve the deployment experience.
So far, we've implemented the autopilot feature using various GitHub Actions triggers and Azure Bicep. So now, when you need to show off your PoC to your clients, as long as anyone can access your repository, they can create resources and deploy the app by themselves without having to learn deployment details. In the next post, let's revise this autopilot feature with no GitHub Actions event triggers.
