In my previous post, I discussed the JavaScript interop feature in Blazor WebAssembly (WASM) and how to leverage it for the Chrome extension development. In this post, I'm going to expand the same extension to support cross-browser compatibility, like Mozilla Firefox, and what to consider for compatibility.
You can download the sample app from this GitHub repository.
Series: Browser Extension with Blazor WASM
- Lift & Shift Existing Chrome Extension to Blazor WebAssembly - Applying Blazor WASM
- Lift & Shift Existing Chrome Extension to Blazor WebAssembly #2 - JavaScript Interop
- Lift & Shift Existing Chrome Extension to Blazor WebAssembly #3 - Cross Browser Compatibility 👈
Browser Extension Polyfill
The Browser Extension Working Group at W3.org proposes the web standards based on the Chrome extension manifest, which supports all web browsers. Based on that proposal, Mozilla has released the Browser Extension Polyfill library that supports the modern promise pattern instead of callback. Therefore, if you import this polyfill library, theoretically, your Chrome extension quickly turns into the browser extension that runs on multiple browser engines.
Therefore, add the polyfill library through CDN to index.html like below. The link takes the latest release of the polyfill.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
...
<body>
<div id="app">Loading...</div>
...
<!-- ⬇️⬇️⬇️ Add this line ⬇️⬇️⬇️ -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/browse/webextension-polyfill/dist/browser-polyfill.min.js"></script>
<!-- ⬆️⬆️⬆️ Add this line ⬆️⬆️⬆️ -->
<script src="_framework/blazor.webassembly.js"></script>
</body>
</html>However, you can't use the direct link to the polyfill because of the "Content Security Policy" violation error.
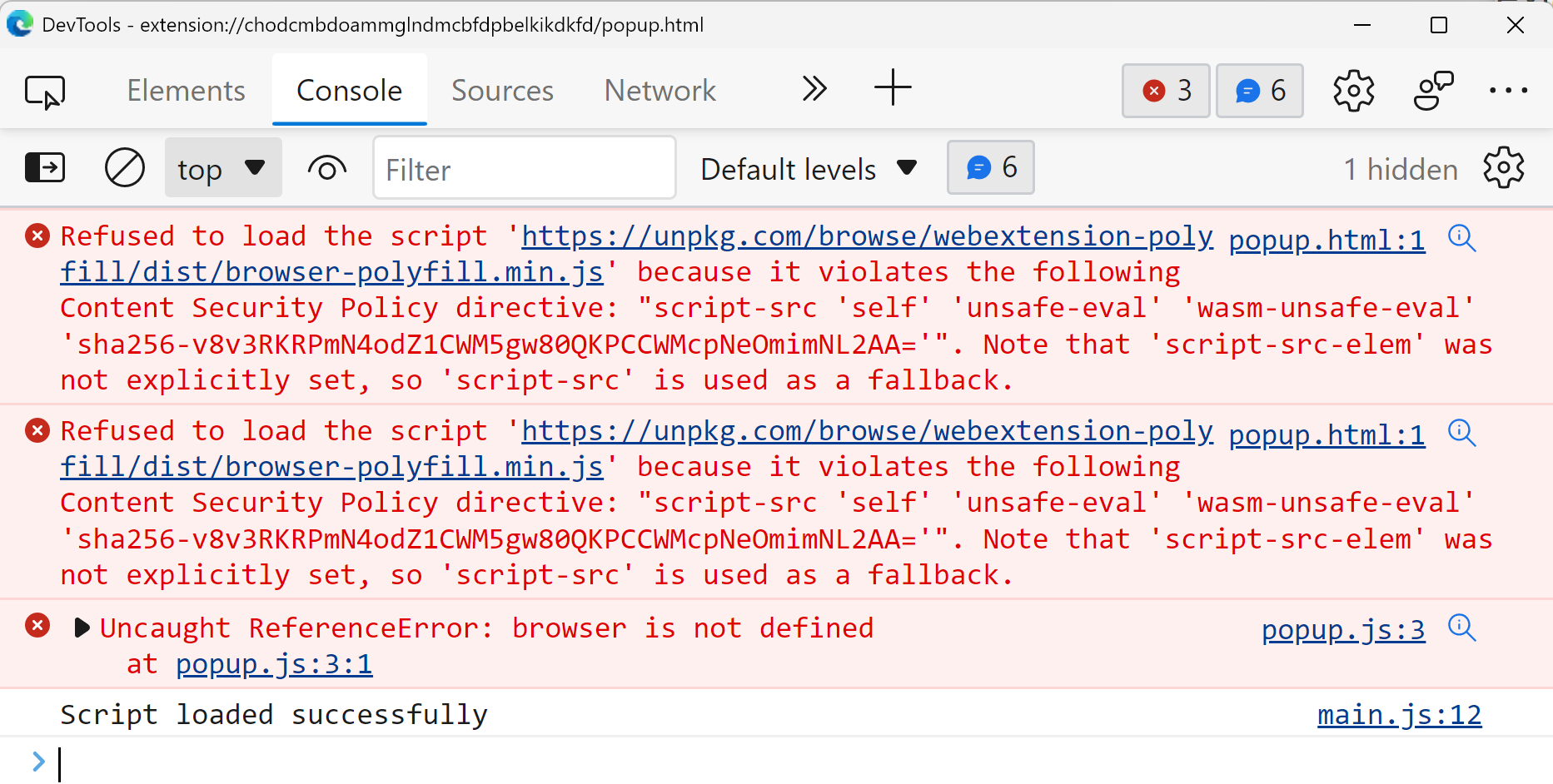
In order to sort out this issue, you should download the JavaScript file and give its local reference. Visit the CDN page and download each files and save them into the wwwroot/js/dist directory. Then, update the index.html file like below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
...
<body>
<div id="app">Loading...</div>
...
<!-- ⬇️⬇️⬇️ Add this line ⬇️⬇️⬇️ -->
<script src="js/dist/browser-polyfill.min.js"></script>
<!-- ⬆️⬆️⬆️ Add this line ⬆️⬆️⬆️ -->
<script src="_framework/blazor.webassembly.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Now, it's OK to use the polyfill. Next, let's move on to manifest.json for cross-browser support.
manifest.json Accommodation
First of all, you need to get rid of Chrome's exclusive features. Especially, as the Declarative Content part only works for the Chrome extensions, you need to replace it with other approaches. In this example, if you want the extension to only work with the domain like developer.chrome.com, developer.mozilla.org or docs.microsoft.com, add domain URLs to the permissions collection like below and remove the declarativeContent value from it.
{
...
"permissions": [
"*://developer.chrome.com/*",
"*://developer.mozilla.org/*",
"*://docs.microsoft.com/*",
"activeTab",
// "declarativeContent",
"storage"
],
...
}Then, add the polyfill to the background script collection.
{
...
"background": {
"scripts": [
"js/dist/browser-polyfill.min.js",
"js/background.js"
],
"persistent": false
},
...
}Initially, manifest.json only uses the options_page attribute, but for compatibility, add the options_ui attribute as well.
{
...
"options_page": "options.html",
"options_ui": {
"page": "options.html",
"browser_style": true
}
...
}And finally, Mozilla-based browsers need a unique ID for each extension. Therefore, give the browser_specific_settings for it.
{
...
"browser_specific_settings": {
"gecko": {
"id": "browser-extension-sample@devkimchi.com"
}
},
...
}Updating manifest.json is over. Now, let's move on to the JavaScript files.
background.js Update
For background.js, you must change all the chrome. instances to the browser. ones because the chrome instances are specific to the Chrome extension, while the browser instances are for the browser extensions in general. In other words, if your background.js looks like the following:
chrome.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(function() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'}, function() {
console.log("The color is green.");
});
chrome.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.removeRules(undefined, function() {
chrome.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.addRules([{
conditions: [
new chrome.declarativeContent.PageStateMatcher({
pageUrl: { hostEquals: 'developer.chrome.com' },
}),
new chrome.declarativeContent.PageStateMatcher({
pageUrl: { hostEquals: 'docs.microsoft.com' },
})
],
actions: [new chrome.declarativeContent.ShowPageAction()]
}]);
});
});All chrome. declared above must be replaced with browser. like below:
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
browser.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(function() {
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
browser.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'}, function() {
console.log("The color is green.");
});
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
browser.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.removeRules(undefined, function() {
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
browser.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.addRules([{
conditions: [
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
new browser.declarativeContent.PageStateMatcher({
pageUrl: { hostEquals: 'developer.browser.com' },
}),
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
new browser.declarativeContent.PageStateMatcher({
pageUrl: { hostEquals: 'docs.microsoft.com' },
})
],
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
actions: [new browser.declarativeContent.ShowPageAction()]
}]);
});
});Once you replace all the chrome instances with browser ones, change all the callback patterns to promise patterns. For example, this example requires the browser's local storage access. How can it be changed?
// Before
browser.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'}, function() {
console.log("The color is green.");
});
// After
browser.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'})
.then(() => {
console.log("The color is green.");
});It's written as an anonymous function and added as the event handler to the onInstalled event. Therefore, it's better to create an independent function like the below:
function handleRuntimeOnInstalled(details) {
browser.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'})
.then(() => {
console.log("The color is green.");
});
}As mentioned above, we can't use the Declarative Content feature any longer. Hence, instead of the events that belong to the declarativeContent property, you need other events and event handlers. This sample extension only works in specific domains like developer.google.com, developer.mozilla.org or docs.microsoft.com, and the declarativeContent property performs this sort of detection. Therefore, replace it with the handleTabs() function like below, using the pageAction property.
function handleTabs() {
browser.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true})
.then((tabs) => {
console.log(tabs[0].url);
let matched = tabs[0].url.includes('developer.chrome.com') || tabs[0].url.includes('developer.mozilla.org') || tabs[0].url.includes('docs.microsoft.com');
if (matched) {
browser.pageAction.show(tabs[0].id);
} else {
browser.pageAction.hide(tabs[0].id);
}
});
}Once everything is done, register both event handlers for the events below:
browser.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(handleRuntimeOnInstalled);
browser.tabs.onActivated.addListener(handleTabs);
browser.tabs.onHighlighted.addListener(handleTabs);
browser.tabs.onUpdated.addListener(handleTabs);popup.js Update
Let's update popup.js. It was initially like this:
let changeColor = document.getElementById('changeColor');
chrome.storage.sync.get('color', function(data) {
changeColor.style.backgroundColor = data.color;
changeColor.setAttribute('value', data.color);
});
changeColor.onclick = function(element) {
let color = element.target.value;
chrome.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true}, function(tabs) {
chrome.tabs.executeScript(
tabs[0].id,
{code: 'document.body.style.backgroundColor = "' + color + '";'});
});
};Like the same in the previous JavaScript file,
- Replace all
chrome.instances withbrowser.ones. - Change all callback patterns to the promise patterns.
let changeColor = document.getElementById('changeColor');
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
// Use the promise pattern
browser.storage.sync.get('color')
.then((data) => {
changeColor.style.backgroundColor = data.color;
changeColor.setAttribute('value', data.color);
});
changeColor.onclick = function(element) {
let color = element.target.value;
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
// Use the promise pattern
browser.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true})
.then((tabs) => {
let matched = tabs[0].url.includes('developer.chrome.com') || tabs[0].url.includes('developer.mozilla.org') || tabs[0].url.includes('docs.microsoft.com');
if (matched) {
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
browser.tabs.executeScript(
tabs[0].id,
{code: 'document.body.style.backgroundColor = "' + color + '";'});
} else {
console.log('URL not matched');
}
});
};The popup.js is done.
options.js Update
This time, it's the turn for options.js, which initially looks like:
let page = document.getElementById('buttonDiv');
const kButtonColors = ['#3aa757', '#e8453c', '#f9bb2d', '#4688f1'];
function constructOptions(kButtonColors) {
for (let item of kButtonColors) {
let button = document.createElement('button');
button.className = 'color-button';
button.style.backgroundColor = item;
button.style.padding = '10px';
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({color: item}, function() {
console.log('color is ' + item);
})
});
page.appendChild(button);
}
}
constructOptions(kButtonColors);- Replace all
chrome.instances withbrowser.ones. - Change all callback patterns to the promise patterns.
let page = document.getElementById('buttonDiv');
const kButtonColors = ['#3aa757', '#e8453c', '#f9bb2d', '#4688f1'];
function constructOptions(kButtonColors) {
for (let item of kButtonColors) {
let button = document.createElement('button');
button.className = 'color-button';
button.style.backgroundColor = item;
button.style.padding = '10px';
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
// Use 'browser.' instead of 'chrome.'
// Use the promise pattern
browser.storage.sync.set({color: item})
.then(() => {
console.log('color is ' + item);
})
});
page.appendChild(button);
}
}
constructOptions(kButtonColors);The options.js file is updated.
Blazor Component Abstraction
Suppose you want to get rid of importing the browser polyfill from index.html and import it directly from the Blazor components. In that case, it's a good idea to create a common page component that each Popup.razor and Options.razor can inherit. First of all, declare a LoadAdditionalJsAsync() method that is called within the OnAfterRenderAsync(...) method.
public class PageComponentBase : ComponentBase
{
protected abstract Task LoadAdditionalJsAsync();
}Then, invoke the method at the end of OnAfterRenderAsync(...). By doing so, the OnAfterRenderAsync(...) method first imports the js/main.js followed by the browser polyfill script, then import the page-specific JavaScript files.
public class PageComponentBase : ComponentBase
{
[Inject]
private IJSRuntime JS { get; set; }
protected IJSObjectReference Module { get; private set; }
protected override async Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender)
{
this.Module = await this.JS.InvokeAsync<IJSObjectReference>("import", "./js/main.js");
var src = "js/dist/browser-polyfill.min.js";
await this.Module.InvokeVoidAsync("loadJs", src);
// Invoke the page-specific JavaScript loader
await this.LoadAdditionalJsAsync();
}
protected abstract Task LoadAdditionalJsAsync();
}With the Popup.razor page, inherit the PageComponentBase class and implement the LoadAdditionalJsAsync() method like below, which imports the js/popup.js file. You don't need the IJSRuntime instance as a dependency any longer, so remove it.
@page "/popup.html"
@* @inject IJSRuntime JS *@
@using ChromeExtensionV2.Components
@inherits PageComponentBase
...
@code {
protected override async Task LoadAdditionalJsAsync()
{
var src = "js/popup.js";
await this.Module.InvokeVoidAsync("loadJs", src);
}
}Similarly, the Options.razor page also inherits the PageComponentBase class and implement the LoadAdditionalJsAsync() method to import js/options.js. The IJSRuntime dependency is no longer necessary, either.
@page "/options.html"
@* @inject IJSRuntime JS *@
@using ChromeExtensionV2.Components
@inherits PageComponentBase
...
@code {
protected override async Task LoadAdditionalJsAsync()
{
var src = "js/options.js";
await this.Module.InvokeVoidAsync("loadJs", src);
}
}Run-PostBuild.ps1 Adjustment
Unlike the Chrome extensions, the Mozilla-based web extension needs a .zip file for installation. Therefore, the PowerShell script, Run-PostBuild.ps1, requires an additional step to generate a .zip file as an artifact.
Compress-Archive -Path ./published/wwwroot/* -DestinationPath ./published/wwwroot/wwwroot.zip -ForceOnce you complete all the steps above, build the project and run the PowerShell script, and it will generate the wwwroot.zip file under the published directory. Next, install the zip file to Firefox, and you will see the screen below:
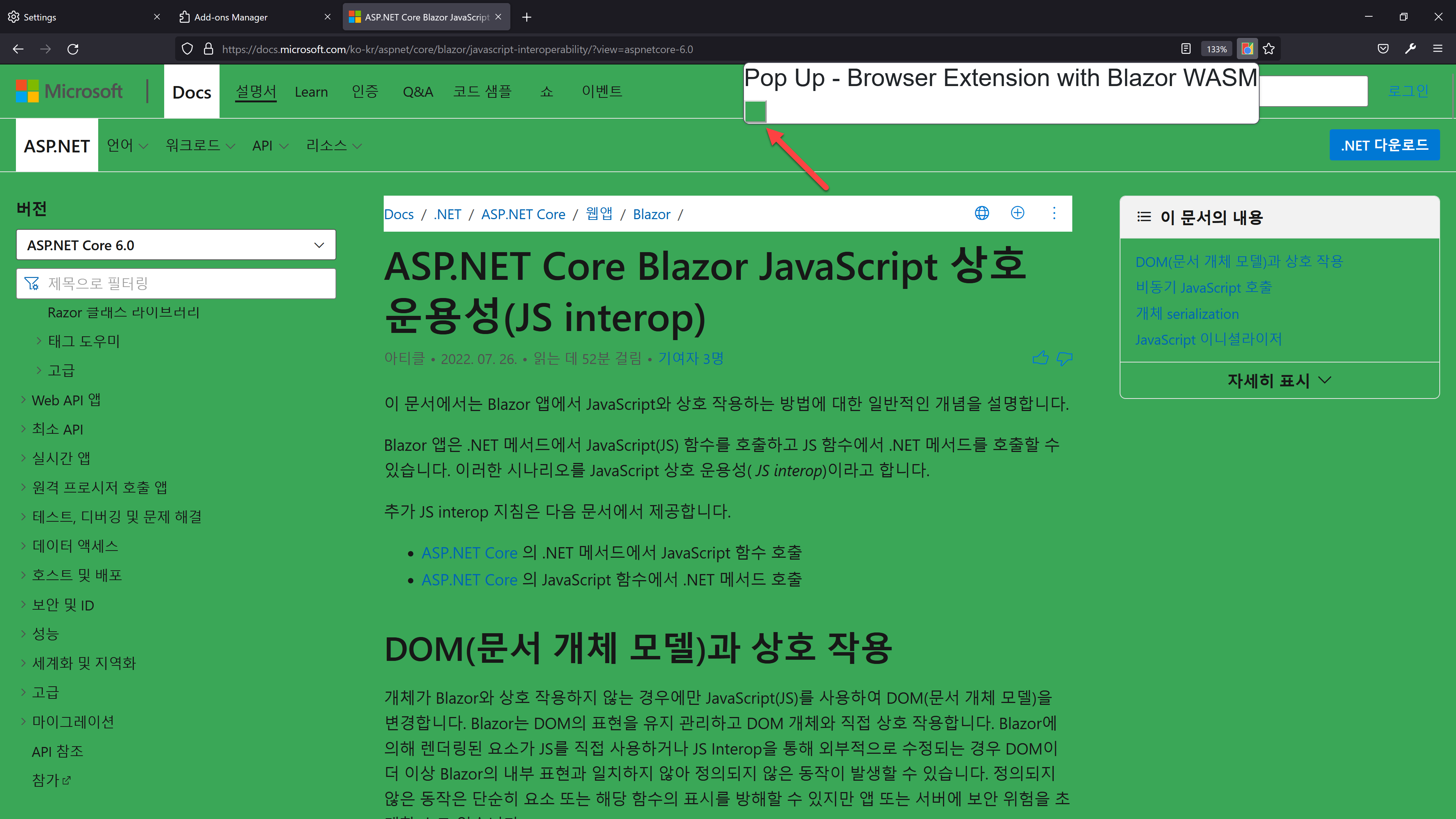
You can see the options page as a pop-up modal due to the manifest.json update. In the options modal, change the background colour to yellow.
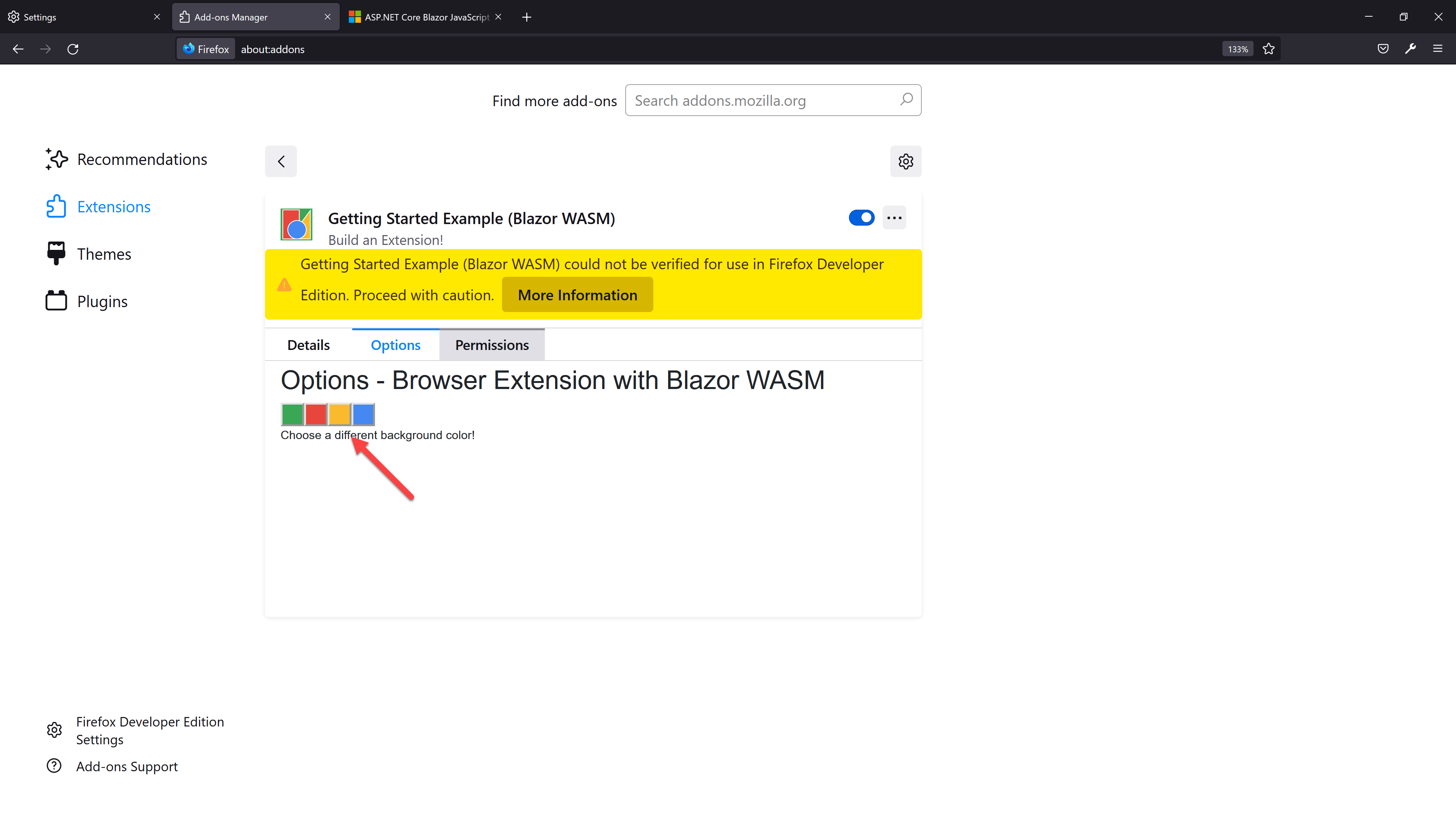
Then, you are able to change the background colour to yellow.
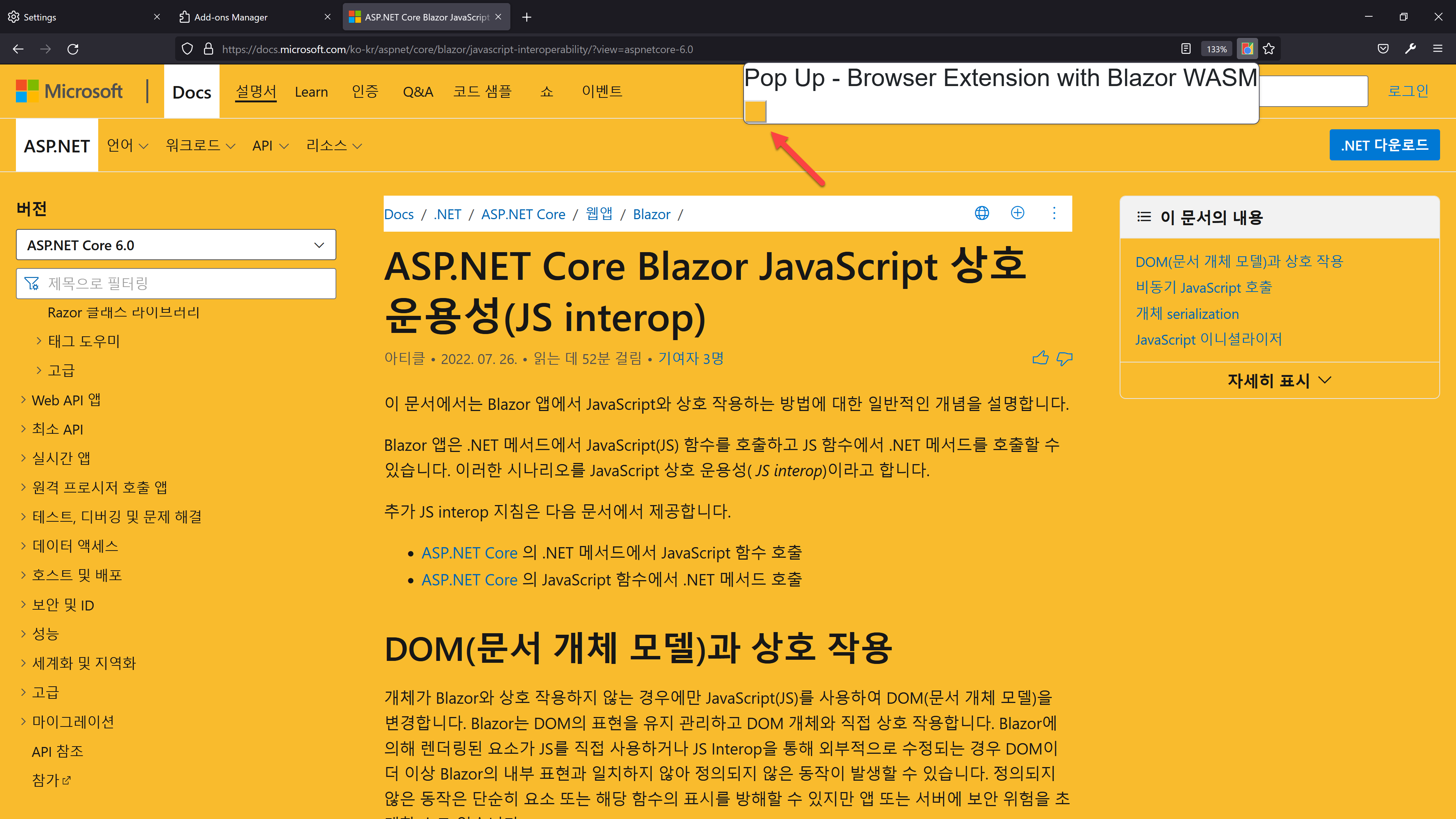
So far, we've walked through how our Blazor WASM-based chrome extension can support cross-browser compatibility and showed how it works on the Firefox browser.
Do you want to know more about Blazor?
Here are some tutorials for you.